Here are details about a :
Space commemorative cover
or Space Cover.
Cosmodrome / Location : China
Date of Cancellation: Mar. 1, 2016
Exist : 2000 copies
Event Type : Launch
Launch Pad / Location : China Taiyuan
Manned / Robotic Mission : Robotic
Mission Objective/Type : Experimental / Science
ou?/where?: au sol - ground
autographe?: non - noneDescription : DAMPE (Dark Matter Particle Explorer) or Wukong is a powerful space telescope for high energy gamma-ray, electron and cosmic rays detection.
It is one of five satellite missions in the framework of the Strategic Pioneer Research Program in Space Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS).
The scientific objectives of DAMPE are to search for and study dark matter particles by conducting high-resolution observation of high-energy electrons and gamma rays, to study the origin of cosmic rays by observing the high energy electrons and heavy nuclei above TeV, and to study the propagation and acceleration mechanism of cosmic rays by observing high-energy gamma rays.
DAMPE will operate at Sun-synchronous orbit with an altitude of 500 km and an inclination of 97.4° with 3-year lifetime. Its total mass is less than 1900 kg, and it will be launched from Jiuquan by a CZ-2D (2) rocket.
There will be five payloads onboard the satellite:
DAMPE consists of a double layer of plastic scintillator strips detector (PSD) that serves as anti-coincidence detector, followed by silicon-tungsten tracker-converter (STK), which is made of 6 tracking double layers; each consists of two layers of single-sided silicon strip detectors measuring the two orthogonal views perpendicular to the pointing direction of the apparatus. Three layers of Tungsten plates with thickness of 1mm are inserted in front of tracking layer 2, 3 and 4 for photon conversion. The STK is followed by an imaging calorimeter of about 31 radiation lengths thickness, made up of 14 layers of Bismuth Germanium Oxide (BGO) bars in a hodoscopic arrangement. A layer of neutron detectors is added to the bottom of the calorimeter. The total thickness of the Bismuth Germanium Oxide calorimeter (BGO) and the STK correspond to about 33 radiation lengths, making it the deepest calorimeter ever used in space. Finally, in order to detect delayed neutron resulting from hadron shower and to improve the electron/proton separation power a neutron detector (NUD) is placed just below the calorimeter. The NUD consists of 16, 1 cm thick, boron-doped plastic scintillator plates of 19.5 × 19.5 cm2 large, each read out by a photomultiplier.
The main scientific objective of DAMPE is to measure electrons and photons with much higher energy resolution and energy reach than achievable with existing space experiments in order to identify possible Dark Matter signatures. It has also great potential in advancing the understanding of the origin and propagation mechanism of high energy cosmic rays, as well as in new discoveries in high energy gamma astronomy.
DAMPE will have unprecedented sensitivity and energy reach for electrons, photons and cosmic rays (proton and heavy ions). For electrons and photons, the detection range is 5 GeV – 10 TeV, with an energy resolution of about 1% at 800 GeV. For cosmic rays, the detection range is 100 GeV – 100 TeV, with an energy resolution better than 40% at 800 GeV. The geometrical factor is about 0.3 m 2 sr for electrons and photons, and about 0.2 m2 sr for cosmic rays. The angular resolution is 0.1° at 100 GeV. Keyword(s) :
#Satellite,
#Telecommunications,
#X-rays, SPACE REVUE : 03 - 2016 Last modified: 07/31/2017 @ 15h59
| Add to cart |
SEE ALSO  |
 |
  |
CHINE 582 | 10,- |
| |
item shown here with picture. |
| |
items related to the item shown. |
|
 See My Cart See My Cart |
|
|

Page : future · Ref: CHINE 582 Space Event :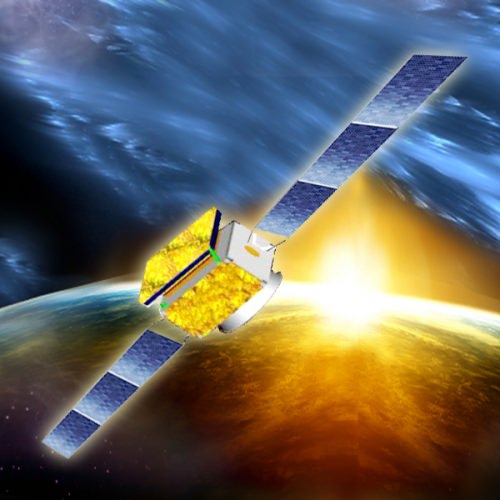 CHINA · DAMPE · WUKONG · DARK MATTER PARTICLE SATELLITE
|